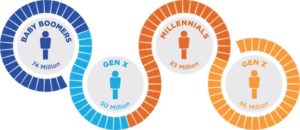
This year, 2024, Gen Zers, who are newly entering the workforce, are expected to outnumber baby boomers in the US workplace. Demographic shifts have always played a crucial role in shaping organizational dynamics in the dynamic landscape of the modern workforce. As we witness the rise of Generation Z (Gen Z) and the gradual exit of Baby Boomers from the workforce, employers face unique challenges and opportunities. This demographic transition not only impacts the composition of the workforce but also necessitates a reevaluation of workplace policies, cultures, and strategies.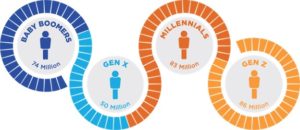
Generation Z, born roughly between the mid-1990s and early 2010s, is now entering the workforce in significant numbers. At the same time, the Baby Boomer generation, born post-World War II between 1946 and 1964, is gradually retiring. This demographic shift has far-reaching implications for employers across various industries. Millennials currently comprise the most significant percentage of the workforce, which will likely remain the case until the early 2040s. However, as Gen Z workers increasingly enter the world of employment – an estimated 23% of the workforce in 2024 – emotional intelligence will be critical to leading effective teams.
Forbes describes Gen Z as “the most diverse and tolerant generation in history,” noting that this generation prioritizes collaboration over competition and self-care over salary. Considering those factors could help employers excel with recruitment and retention. Here is Gen Z’s contribution to the workforce and how it can excel in the workplace:
- Digital Natives vs. Digital Immigrants: Gen Z is the first generation to grow up entirely in the digital age, while Baby Boomers may still be adapting to rapidly evolving technology. This contrast presents both challenges and opportunities for employers. Companies must invest in digital literacy training for older workers while leveraging the tech-savvy nature of Gen Z employees to drive innovation and digital transformation within the organization.
- Workplace Expectations: Gen Z brings unique expectations regarding work-life balance, career progression, and workplace culture. They prioritize flexibility, purpose-driven work, and continuous learning and development opportunities. Employers must align their policies and practices with these expectations to attract and retain top Gen Z talent.
- Leadership Transition: With Baby Boomers retiring, organizations face the challenge of transferring knowledge and leadership skills to the next generation of leaders. Succession planning becomes crucial to ensure a smooth transition and continuity in leadership. Mentoring programs that facilitate knowledge transfer from experienced Baby Boomers to younger employees can prove invaluable.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Gen Z is known for its strong emphasis on diversity and inclusion. Employers must prioritize creating inclusive work environments that embrace diversity in all its forms. This includes addressing unconscious bias, promoting equitable opportunities for career advancement, and fostering a culture of belonging where every employee feels valued and respected.
- Communication Preferences: Gen Z prefers concise, direct communication, often utilizing digital channels such as instant messaging and social media. Employers need to adapt their communication strategies to accommodate these preferences while recognizing the value of face-to-face interactions, especially for building strong interpersonal relationships and fostering collaboration.
- Impact on Consumer Trends: As Gen Z becomes a dominant consumer demographic, employers must understand their preferences, values, and purchasing behaviors. This understanding is crucial for developing products and services that resonate with Gen Z consumers and maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
In conclusion, the transition as Gen Z outnumbers Baby Boomers in the workforce presents a multifaceted challenge for employers. Adapting to Gen Z’s unique characteristics and expectations while effectively managing Baby Boomers’ departure requires strategic foresight, agility, and a commitment to fostering a diverse, inclusive, and dynamic workplace culture. By embracing this demographic shift and leveraging each generation’s strengths, employers can position themselves for success in the evolving landscape of the modern workforce.
Re: Glassdoor’s Economic Research team identified the following three trends for 2024
